SenseCAP LoRaWAN IIoT Solutions for OPEN Global IoT Education Project for Future Jobs and Resilient Livelihoods
By Ye Seong SHIN 2 years agoIn the OPEN Global IoT Education Project, SenseCAP LoRaWAN IIoT solution has been deployed in order to help solve diverse local challenges for children and local communities towards a sustainable and resilient world. Through their participation, they are self-empowered to learn specific skills to prepare for newly emerging jobs in the future. In this way, the Project aims to achieve the UN’s SDGs 4, 5, 12, 11, 13, 9, 8, 17, 6, 7, 14, 15, 2 and 1.
Project Name: OPEN Global IoT Education Project
Deployment Location: USA, Australia, DRC, Liberia, Kenya, Malawi, Nigeria, Haiti
Targeted Industry Type: Education
Project Partner(s): 
Last year, the World Economic Forum (WEF) shared an alarming status of the world’s employment in its third edition of “The Future of Jobs Report 2020”: 50% of all employees will need to reskill by 2025 due to humanity’s rapid technological advancement. The skills we need to learn are referred to as “future skills”, which are classified into 4 dimensions: problem-solving, self-management, working with people, and technology use and development (Figure 1). WEF highlights that adoption of the future skills is vital, if we want to smoothly integrate into the emerging job landscape and not to be replaced by machine labor. The jobs on increasingly growing demand include specialists, developers, and analysts in IoT, AI and machine learning, big data, software and applications, process automation, digital transformation, information security, sustainable business development, and digital marketing. (Whiting, 2020; WEF, 2020). The advancement of job automation doubled with the COVID-19’s impact on the world not only disrupts our careers, but also our lifestyles, industries, and education.

Figure 1. Top 10 Future Skills We Need to Prepare by 2025 (WEF, 2020)
What’s the Challenge?
How to support future skills of children and adults to prepare for opportunities in this increasingly transformative world?
What’s the Project About?
In 2020, Seeed joined the partnership with One Planet Education Network (OPEN) for the “Global IoT Education Project”, which is aimed at bringing the next-generation technologies to classrooms and local communities for future skills development (Figure 2). This Project seeks to facilitate students and local residents to learn about real-world challenges and issues – like water shortage, environmental degradation and monitoring, climate change impact adaptation, sustainable agriculture, social challenges, and school connectivity – that share a close link with the UN’s SDGs. Then, all participants will be guided to solve such issues. OPEN selected our SenseCAP IIoT devices and Helium for this Project, in which the SenseCAP LoRaWAN series functions as an integral part within OPEN’s different curricula on sustainable agriculture and forestry, smart gardening, and vertical hydroponics, among other things.
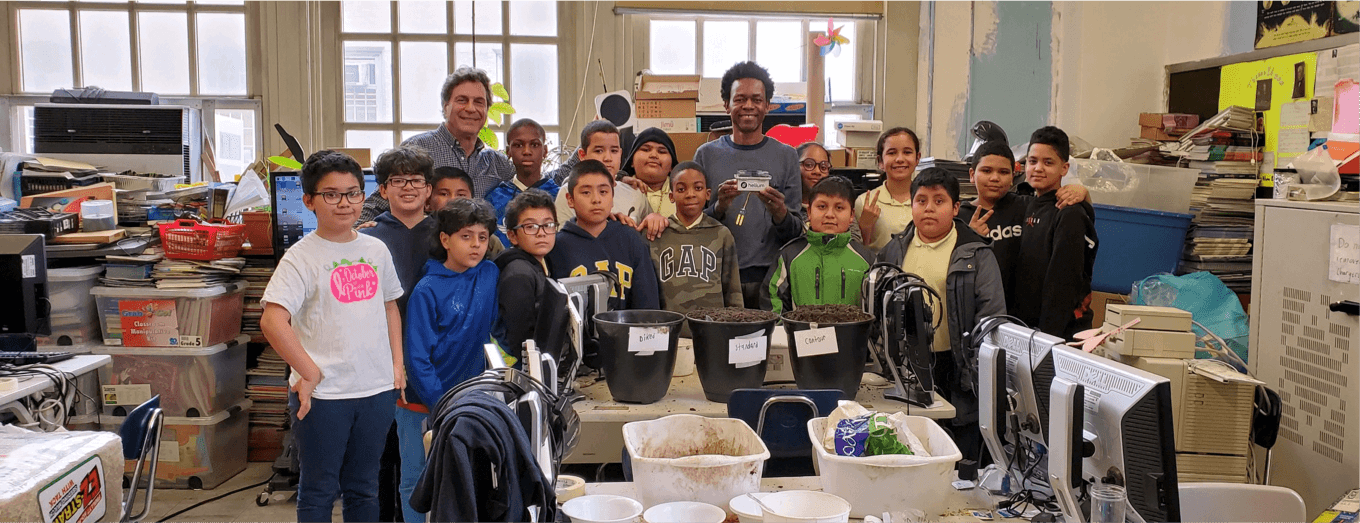

Figure 2. OPEN IoT Education Projects Settled in a Classroom in New York Timothy Dwight Elementary School Facilitated by Dr. Wednaud J. Ronelus (Alchemist Club School & Studios, n.d.)
Headquartered in Scituate Town of Massachusetts in the USA, OPEN is a social enterprise and a leading provider of educational programs. The program aims to engage and inspire all children and adults to develop future skills, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and constructive analysis. Such a pragmatic skill set is vitally needed to tackle sustainability issues of local communities and the world. Therefore, OPEN challenges all learners with programs that stimulate 24/7 passion for the skills development and lifelong learning. Through their programs, they facilitate self-empowerment of the learners to prepare for the upcoming world filled with new transformations, industries, and opportunities. OPEN’s mission is to innovate the traditional teaching and learning by harnessing emerging technologies like IoT, AI, Machine Learning, VR, and AR. They focus on the learning-by-doing or applied sciences concept, that facilitates the learners to directly test and apply their learnings in real life to solve the glocal agenda.
Ever since its foundation in 2013, Helium is a company committed to building the world’s first peer-to-peer wireless networks, and to build connected devices more easily. Helium provides long-range, low-power, bi-directional communications for LoRaWAN devices. Its innovation, “Helium Blockchain”, is designed to support more efficient and secure application networks, while rewarding anyone who acts as a network operator. Hence, Helium is also known as “The People’s Network”.
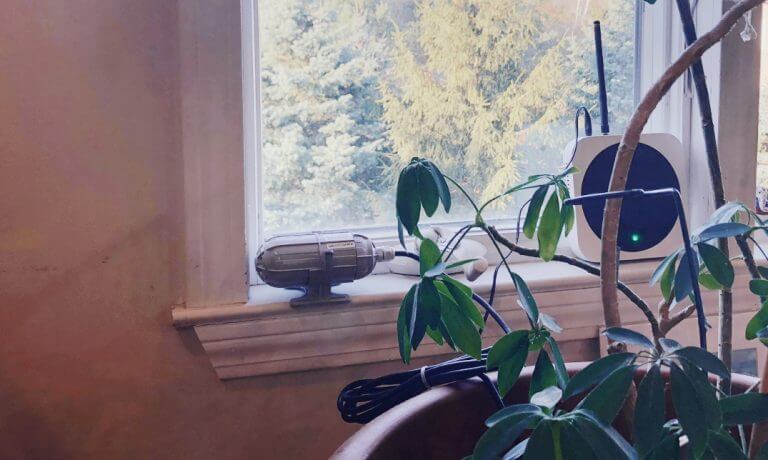

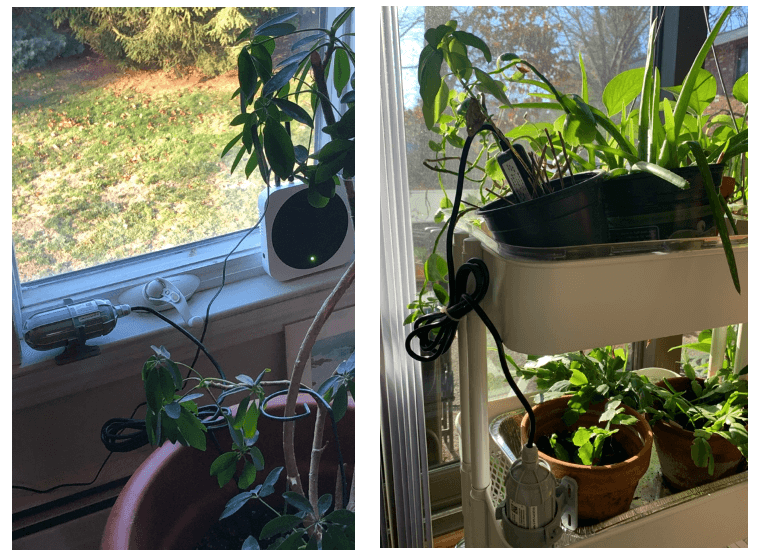
Figure 3. SenseCAP Soil Moisture & Temperature Sensors Deployed in New York During the COVID-19
In the OPEN Global IoT Education Project, SenseCAP LoRaWAN sensors, including light intensity sensor, soil moisture and temperature sensor, were deployed for: i) soil experimentation indoors; ii) outdoor testing plots, and; iii) hydroponics projects at several schools and different sites in New York and Massachusetts of the USA, as well as at schools in New South Wales of Australia (Figure 3 above). Since SenseCAP sensors are characterized with great interoperability with other LoRaWAN devices, they work well with Helium, because the two will produce the synergy effects in making the learners’ network communications more convenient.
So, how does this work? First, SenseCAP sensors monitor and collect data of the above-mentioned elements’ parameters critical to the growth of plants. Then, the collected data is transmitted to Helium’s hotspots and to the Cloud Server through the SenseCAP LoRaWAN gateway. This Cloud Server’s data is updated on Helium’s data platform, which is shared with students participating in the Project and other OPEN educational programs, as well as with OPEN-supporting scientists globally (Figure 4). By making the data available for students in OPEN’s partner schools around the world, it provides common platforms and opportunities for the students and local communities, where they share project observations, knowledge, skills, and experience in solving similar SDG challenges. This is a good example of glocal community-applied learning, empowered by OPEN’s broad school networks. What’s more, OPEN Global IoT Education Project will contribute to achieving the UN’s 2030 Agenda of SDGs.
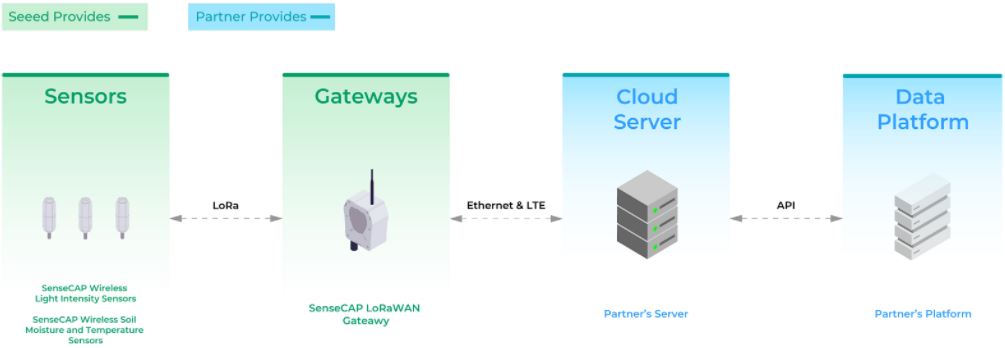
Figure 4. System Deployment Diagram of OPEN IoT Education Project
In case you are interested in making this kind of IoT projects for educational purposes, you can find out the SenseCAP LoRaWAN devices deployed in this Global IoT Education Project in the following:
- SenseCAP Outdoor Gateway – LoRaWAN
- SenseCAP Wireless Light Intensity Sensor – LoRaWAN
- SenseCAP Wireless Soil Moisture & Temperature Sensor – LoRaWAN
After deploying Seeed’s IIoT devices for a while, the Founder and CEO of OPEN, George Newman, shared his experience on collaborating with Seeed by elaborating why they selected us as a partner:
“We selected Seeed Studio and their industrial-level technologies for their quality, durability, form factor, ease of use, and very affordable cost. Having worked with Seeed over the intervening months, it is truly their service that sets them apart: From the sales to the technical and support teams, they are a gold standard for others in the industry! They are incredibly responsive, thorough, and flexible in dealing with changing customer needs, and for custom development. The staff is so nice and polite, they are a joy to work with on a regular basis.”
“We work in primary to secondary education internationally and the Seeed team has been so supportive in getting us set up in the early stages, as some teachers who are our end users are sometimes not that technically sophisticated. So patience is a word that comes to mind as well. IoT is central to our future STEM education programs and for 21st-century schooling. So we look forward to a long-term partnership with Seeed as our STEM Learning and education technology business expands, and our application set grows.”
In the near future, Seeed’s SenseCAP LoRaWAN sensors will be deployed in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) to detect CO2 concentration level, in order to provide precious data on monitoring possible volcano eruptions in Goma City. With the data insights, SenseCAP series will help prepare local communities to devise evacuation plans in advance. Currently, OPEN’s curricula and projects are in action in more than 40 schools in the USA, Australia, Liberia, DRC, Kenya, Malawi, Nigeria, and Haiti. OPEN has plans to be available in China, Thailand, Japan, Mali, and other countries in the near future. We are happy to be a part of this great partnership, and looking forward to closely collaborating with OPEN, together with other partners such as Helium, to promote scientific and technological literacy in different continents and cultures.
Which SDGs Are Relevant?
Now, when we consider the connection between the OPEN Global IoT Education Project with SDGs, it is obvious that it mainly promotes SDG 4 on Quality Education. However, we would like to share that the Project contributes to far more SDGs than what you probably have anticipated (Figure 5):

Figure 5. SDGs Supported by OPEN Global IoT Education Project (UN, 2016)
Indeed, contribution to 14 SDGs is a great achievement, but what are the implications of achieving those goals? To understand the dynamic and holistic relationship among all the SDGs above, you can take a look at their specific Targets of each SDG:
- Secure that all children have free, equitable and quality primary and secondary education (Target 4.1)
- Greatly augment the number of young people and adults (including the ones vulnerable situations) who have technical and vocational skills for employment by guaranteeing equal access to education, and by eradicating gender disparities (Targets 4.4 & 4.5)
- Scale-up the usage of ICTs to foster empowerment of women (Target 5.B)
- Make sure that all learners obtain relevant skills and knowledge needed for achieving sustainable development and sustainable lifestyle (Targets 4.7 & 12.8)
- Lower the adverse per capita environmental impact of urban areas, i.e., air quality and waste management, as well as greatly augment the number of cities implementing integrated practices for adaptation and mitigation to climate change, resilient livelihoods, and resource efficiency (Targets 11.6 & 11.B)
- Reinforce resilience and adaptive capacity to climate change (mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction and prevention) by means of education, awareness-raising campaigns, and other methods for effective capacity building (Targets 13.1, 13.3, 13.B &1.5)
- Promote sustainable and resilient infrastructure for human well-being and economic growth via innovation and ICTs (Targets 9.1 & 8.2)
- Implement programs on sustainable consumption and production to efficiently use resources, and reduce/reuse/recycle wastes (Targets 12.1, 12.2, 12.3, 12.5 & 8.4)
- Support developing countries to build scientific and technological capacity (Targets 12.A & 17.9)
- Develop global strategies for youth employment (Target 8.B)
- Upgrade regional, global, and multi-stakeholder (public-private-civil society) cooperation for making science, innovation, and technology accessible, especially environmentally-sound technologies (Targets 17.6, 17.7, 17.16 & 17.17)
- Ensure universal access to clean and affordable drinking water and electricity, by improving their quality and efficiency (Targets 6.1, 6.3, 6.4, 7.1 & 7.3)
- Foster local communities’ participation in enhancing quality of water and sanitation facilities (Target 6.B)
- Decrease and prevent marine pollution, deforestation, and desertification, as well as safeguard marine/mountain/terrestrial/natural ecosystem (Targets 14.1, 14.2, 14.3, 15.2, 15.3. 15.4 & 15.5)
- Reinforce capacity building for managing national and global health risks (Target 3.D)
- Eradicate hunger and extreme poverty, and increase agricultural productivity by value-added commodities to foster sustainable food production and resilient agricultural practices (Targets 2.1, 2.3, 2.4 & 1.1)
By making educational programs and technological resources accessible for schools and local communities, Seeed and OPEN are facilitating self-empowerment of teachers, students, and local residents in different parts of the world to explore science, mathematics, music, arts, and humanities with IoT solutions. As Patrick Dixon – one of the world’s renowned futurists and trends analysts – passionately disseminates, “The key to understanding the future is one word: sustainability” enabled by sustainagility. Yes, together with our partners, Seeed is dedicated to providing technical support for our partners to build a sustainable and resilient future for all. Stay tuned for more updates on further cooperation with OPEN and Helium! 🙂
About Author
Ye Seong SHIN
Sustainability and CSR Manager at Seeed Studio
。
Jointly organize/participate in multi-stakeholder projects/platforms/events/webinars/workshops/hackathons/etc. to accelerate SDGs with local communities and open tech anywhere in the world by connecting with Ye Seong SHIN today on LinkedIn.
。
Seeed Studio is the IoT and AI solution provider for all types of traditional industries’ sustainable digitalization. Since its establishment in 2008, Seeed Studio’s technological products and customization services are used for smart agriculture, smart cities, smart environmental monitoring, smart animal farming, smart aquaculture, meteorological monitoring, STEAM education, and all types of emerging scenarios enabled by the Industry 4.0. With the company’s mission to “Empower Everyone to Achieve Their Digital Transformation Goals” (which shares similar values with SDGs’ Motto of “Leave No One Behind”), Seeed Studio is devoted to using open source technologies for accelerating SDGs with multi-stakeholders from UN agencies, academia, companies, CSOs, governments, public/private organizations, and so on. This is why, Seeed Studio also founded “Chaihuo Maker Space”, and started China’s first Maker Movement by annually organizing “Maker Faire Shenzhen”.